Neutering, a common veterinary procedure, plays a significant role in the responsible care and management of companion animals. It involves the surgical removal of reproductive organs in male and female animals, ultimately preventing them from reproducing. This is a crucial aspect of pet health, behavior, and population control. In this exploration, we delve into the reasons behind this procedure , the benefits it offers, the differences between neutering and spaying, as well as the various considerations and misconceptions surrounding this procedure. By gaining a deeper understanding of this, pet owners can make informed decisions that contribute to the overall health and happiness of their furry companions while also positively impacting the larger animal community.
1. Understanding Neutering: Exploring the Basics
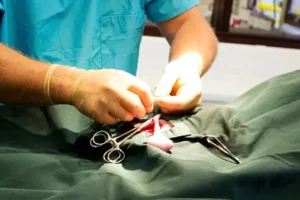
Neutering, a fundamental aspect of responsible pet ownership, is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of reproductive organs in animals. This procedure is most commonly performed on dogs and cats, although it can be applied to other companion animals as well. It is carried out for various reasons, including health benefits, behavior modification, and population control.
In male animals, it is often referred to as castration, involves the removal of the testicles. This procedure eliminates the production of sperm and significantly reduces the production of male hormones such as testosterone. By doing so, it can have a positive impact on certain behavioral issues, such as aggression and territorial marking. Additionally, it can reduce the risk of certain health problems, including testicular cancer and prostate issues.
In female animals, it is commonly known as spaying, which involves the removal of the ovaries and usually the uterus. Spaying eliminates the heat cycle, preventing unwanted pregnancies and reducing the risk of uterine infections and certain types of cancers. Furthermore, spaying can help curb certain undesirable behaviors linked to the heat cycle, such as restlessness and excessive vocalization.
This procedure is also plays a vital role in addressing the issue of pet overpopulation. By preventing animals from reproducing, it helps control the number of homeless animals in shelters and on the streets. This, in turn, alleviates the strain on animal rescue organizations and promotes a healthier environment for both pets and humans.
While neutering offers numerous benefits, it’s essential for pet owners to make informed decisions. Consulting with a veterinarian is crucial before opting for the procedure. The timing of neutering can vary depending on the species, breed, and individual health considerations. Veterinarians can provide guidance on the most suitable timing for it, taking into account factors such as the animal’s age, size, and overall health.
In conclusion, understanding the basics of neutering is essential for pet owners who are committed to the well-being of their animals and the broader community. This surgical procedure not only improves the health and behavior of pets but also contributes to the larger goal of controlling the pet population and promoting responsible pet ownership.
2. The Benefits of Neutering Your Pet: Health and Behavior
Neutering and spaying are two distinct surgical procedures aimed at controlling the reproductive capacity of pets, but they apply to different genders—neutering for males and spaying for females. While both procedures share the common goal of preventing unwanted pregnancies and certain health issues, they involve the removal of different reproductive organs and come with their own unique benefits and considerations.
Often referred to as castration, is the surgical removal of a male animal’s testicles. This procedure eliminates the production of sperm and significantly reduces the levels of testosterone, the male hormone responsible for various mating behaviors. By neutering male pets, owners can witness positive changes in behavior, such as reduced aggression, territorial marking, and roaming tendencies. Additionally, neutering has been linked to a decreased risk of testicular cancer and certain prostate problems, contributing to the long-term health and well-being of the animal.
On the other hand, spaying involves the removal of a female animal’s ovaries and often the uterus. This procedure prevents the animal from going into heat and eliminates the possibility of pregnancy. Spaying offers numerous health benefits, including a significant reduction in the risk of mammary gland tumors and uterine infections. Moreover, spayed females are spared the physical and emotional stress of pregnancy and birth, enhancing their overall quality of life.
It’s important to note that both neutering and spaying procedures are typically performed under general anesthesia by a licensed veterinarian. The timing of these procedures can vary depending on the species, breed, and individual animal’s age and health. Many experts recommend spaying or neutering pets before they reach sexual maturity to maximize the health and behavioral benefits. However, recent research suggests that there may be benefits to delaying the procedure slightly to allow for proper growth and development.
In conclusion, while neutering and spaying serve distinct purposes for male and female pets, respectively, both procedures contribute to the overall well-being of animals and help manage pet populations. Pet owners should consult with their veterinarian to determine the best timing and approach for these surgeries based on their pet’s individual needs and circumstances, ultimately promoting a healthier and happier life for their beloved companions.
3. Neutering vs. Spaying: Differentiating Between Male and Female Procedures
Neutering and spaying are two distinct surgical procedures aimed at controlling the reproductive capacity of pets, but they apply to different genders—neutering for males and spaying for females. While both procedures share the common goal of preventing unwanted pregnancies and certain health issues, they involve the removal of different reproductive organs and come with their own unique benefits and considerations.
Often referred to as castration, is the surgical removal of a male animal’s testicles. This procedure eliminates the production of sperm and significantly reduces the levels of testosterone, the male hormone responsible for various mating behaviors. By neutering male pets, owners can witness positive changes in behavior, such as reduced aggression, territorial marking, and roaming tendencies. Additionally, neutering has been linked to a decreased risk of testicular cancer and certain prostate problems, contributing to the long-term health and well-being of the animal.
On the other hand, spaying involves the removal of a female animal’s ovaries and often the uterus. This procedure prevents the animal from going into heat and eliminates the possibility of pregnancy. Spaying offers numerous health benefits, including a significant reduction in the risk of mammary gland tumors and uterine infections. Moreover, spayed females are spared the physical and emotional stress of pregnancy and birth, enhancing their overall quality of life.
It’s important to note that both neutering and spaying procedures are typically performed under general anesthesia by a licensed veterinarian. The timing of these procedures can vary depending on the species, breed, and individual animal’s age and health. Many experts recommend spaying or neutering pets before they reach sexual maturity to maximize the health and behavioral benefits. However, recent research suggests that there may be benefits to delaying the procedure slightly to allow for proper growth and development.
Ainu Dog: 14 Most Important Facts
4. Neutering Surgery: What to Expect Before, During, and After
Neutering surgery is a common and routine procedure performed by veterinarians to sterilize pets, both male and female, by removing their reproductive organs. This surgical intervention offers numerous benefits for pets’ health, behavior, and overall well-being, while also playing a crucial role in controlling the pet population. Understanding the process of neutering, from preparation to recovery, can help pet owners make informed decisions and provide optimal care for their beloved companions.
Before the Surgery: Preparing Your Pet and Yourself
Before the this procedure, your veterinarian will typically conduct a comprehensive health assessment to ensure your pet is fit for surgery. This may involve blood tests, physical examinations, and discussions about the surgical process. You’ll receive instructions regarding fasting and medication administration to ensure your pet’s safety during anesthesia.
Pet owners should mentally prepare for the surgery as well. While the procedure is routine, it’s natural to feel a mix of emotions. Reassure yourself that neutering is a responsible choice that benefits your pet’s long-term health and reduces the risk of certain reproductive-related illnesses.
During the Surgery: A Skilled and Careful Procedure
Neutering surgery is performed under general anesthesia, ensuring your pet is comfortable and pain-free throughout the procedure. For males, the testicles are removed through a small incision in the scrotum. For females, the ovaries and uterus are removed through a similar incision in the abdominal area.
Veterinary surgeons follow strict protocols to minimize risks and complications. Monitoring equipment tracks vital signs such as heart rate and oxygen levels, ensuring the procedure is safe and successful.
After the Surgery: Providing Post-Operative Care
After the surgery, your pet will need a calm and comfortable environment for recovery. You might notice some grogginess as the anesthesia wears off, but this is normal. Your veterinarian may prescribe pain medication and provide instructions on wound care.
Monitor your pet closely during the recovery period. Prevent licking or biting at the incision site, and ensure they don’t engage in vigorous activities. A post-surgery checkup allows the veterinarian to assess healing and address any concerns.
In conclusion, neutering surgery is a vital step in responsible pet ownership. By understanding the preparation, procedure, and post-operative care, you can confidently provide your pet with the best possible experience. It not only contributes to your pet’s health and behavior but also plays a vital role in controlling the pet population and promoting the well-being of animals overall.
5. Neutering and Population Control: Addressing Overpopulation Concerns
The issue of pet overpopulation is a pressing concern that affects animal welfare and communities worldwide. Uncontrolled breeding leads to an influx of unwanted and homeless animals, straining animal shelters, resources, and posing ethical and public health challenges. It, also known as sterilization, is a fundamental tool in addressing this issue and is pivotal in curbing the rampant overpopulation of pets.
It is a proactive approach to preventing unwanted litters, as it renders animals incapable of reproducing. This is particularly crucial in the case of cats and dogs, whose reproductive capacities can lead to exponential population growth if left unchecked. Male animals are neutered by removing their testicles, while female animals undergo spaying, which involves the removal of their ovaries and sometimes the uterus. These procedures not only prevent reproduction but also offer numerous health benefits, such as reducing the risk of certain cancers and infections.
One of the most significant advantages of neutering is its role in controlling the population of stray and feral animals. Stray animals often struggle to find adequate food, shelter, and medical care, leading to suffering and public health concerns. Neutering these animals helps break the cycle of reproduction and reduces the number of future generations of strays. Additionally, neutering feral cats through trap-neuter-return (TNR) programs has proven effective in stabilizing and eventually decreasing feral cat populations in communities.
By addressing overpopulation through this procedure, communities can alleviate the burden on animal shelters and rescue organizations. Shelters often become overcrowded with unwanted animals, leading to euthanasia as a means of population control. It helps reduce the inflow of new animals to shelters, allowing these organizations to focus on finding loving homes for the animals already in their care.
In conclusion, it plays a vital role in controlling pet overpopulation and its associated challenges. By preventing unplanned litters and reducing the number of stray and feral animals, neutering not only improves the overall welfare of individual animals but also contributes to the well-being of communities as a whole. Responsible pet ownership, combined with accessible and affordable neutering programs, can pave the way toward a more compassionate and sustainable solution to the problem of pet overpopulation.
6. Health Implications of Neutering: Risks, Myths, and Facts
It is commonly performed surgical procedure in veterinary medicine, has been associated with numerous health implications, some of which are rooted in myths while others are supported by scientific evidence. This article aims to shed light on the risks, myths, and facts surrounding neutering’s impact on the health of pets.
Myth: Neutering Causes Weight Gain
One prevailing myth suggests that neutering leads to excessive weight gain in pets. While neutering can affect metabolism and energy levels, weight gain is primarily a result of diet and exercise. Responsible pet owners can prevent weight gain by providing a balanced diet and regular physical activity.
Fact: Reduced Risk of Reproductive Cancers
This procedure significantly decreases the risk of reproductive-related cancers in both male and female pets. In females, spaying virtually eliminates the risk of ovarian and uterine cancers, while in males, it reduces the likelihood of testicular cancer. This preventive measure contributes to a longer and healthier life for pets.
Myth: It’s Causes Joint Problems
A common misconception suggests that neutering can lead to joint issues, particularly in larger dog breeds. However, scientific research has not established a direct link between neutering and joint problems. Genetics, nutrition, and exercise play more substantial roles in joint health.
Fact: Reduced Behavioral Issues
Neutering can positively influence behavior by reducing aggression, marking, and roaming tendencies in male pets. In female pets, it eliminates the heat cycle, which can lead to restlessness and unwanted behaviors. However, behavioral changes may vary depending on the individual animal’s temperament.
Myth: Early Neutering Stunts Growth
Some believe that neutering at a young age can stunt a pet’s growth. While early neutering may slightly affect growth plate closure, the overall impact on growth is minimal and varies among different species and breeds.
Fact: Population Control and Overpopulation
It plays a crucial role in curbing pet overpopulation. By preventing unplanned litters, neutering contributes to reducing the number of homeless animals and the strain on animal shelters and resources.
In conclusion, understanding the health implications of neutering requires separating myths from facts. While certain misconceptions persist, scientific evidence overwhelmingly supports the benefits of neutering, including the reduced risk of reproductive cancers, improved behavior, and vital contributions to population control. Pet owners should consult with their veterinarians to make informed decisions based on their pets’ individual needs and circumstances. Responsible neutering remains an essential component of promoting the overall health and well-being of companion animals.
Cat Spaying: 10 Important Impacts
7. Behavioral Changes After Neutering: Separating Fact from Fiction

It is the surgical alteration of an animal’s reproductive organs, is often associated with a range of behavioral changes. While some of these changes are grounded in scientific evidence, others have become entangled with myths and misconceptions. It’s crucial for pet owners to discern between fact and fiction to make informed decisions about their pets’ well-being.
Factual Behavioral Changes:
- Reduced Aggression: Neutering can lead to a decrease in aggressive behaviors, particularly in male animals. Testosterone, a hormone produced by the testes, is linked to territorial and aggressive tendencies. Neutering significantly lowers testosterone levels, contributing to a calmer and less confrontational demeanor.
- Roaming and Marking: Neutering can curtail the inclination to roam and mark territory with urine. Male animals, especially cats and dogs, often engage in scent-marking behaviors to establish their territory. It can mitigate these instincts, resulting in a more content and home-bound pet.
- Social Interactions: Neutered animals tend to exhibit improved social interactions with other animals. They are often more amiable and less inclined to engage in dominance-related confrontations, leading to smoother integration into multi-pet households.
Debunking Myths:
- Weight Gain: While neutered animals may experience a slightly reduced metabolic rate, weight gain is not solely a result of neutering. Appropriate diet and exercise are key factors in maintaining a healthy weight for pets.
- Personality Alteration: Neutering does not fundamentally alter a pet’s core personality traits. Individual temperament remains largely intact, though some behaviors linked to reproductive hormones may diminish.
- Training Effectiveness: Neutering alone is not a cure-all for behavior problems. Training and socialization play pivotal roles in shaping a pet’s behavior, regardless of their reproductive status.
- Stunting Growth: It does not inherently stunt a pet’s growth. Growth plates close with age, and it’s timing can be crucial to ensure proper development.
In conclusion, while factual behavioral changes are associated with neutering, it’s essential to dispel common myths. Neutering can indeed bring about positive behavioral adjustments, but it is not a catch-all solution for every behavioral issue. Responsible pet ownership involves a holistic approach that combines appropriate medical care, training, and socialization. By understanding the genuine effects of neutering on behavior, pet owners can provide the best possible care for their beloved companions.
8. Neutering’s Role in Preventing Reproductive-Related Health Issues
It is a surgical procedure involving the removal of reproductive organs, serves a crucial role in preventing a range of reproductive-related health issues in pets. While primarily known for its contribution to population control and behavioral modifications, neutering significantly impacts the long-term well-being of both male and female animals.
One of the most significant benefits of neutering is the reduction in the risk of certain cancers and reproductive disorders. In male pets, neutering, also known as castration, involves the removal of the testicles. This procedure drastically lowers the chances of testicular cancer, a potentially fatal condition. Additionally, neutering curbs the risk of prostate problems and eliminates the possibility of testicular torsion, a painful and emergent condition.
For female animals, neutering, or spaying, involves the removal of the ovaries and often the uterus. This procedure virtually eliminates the risk of ovarian and uterine cancers, which can be life-threatening. Furthermore, spaying significantly reduces the likelihood of mammary gland tumors, particularly if performed before the first heat cycle. These tumors are often malignant in nature and can metastasize rapidly.
It is also addresses a host of reproductive-related health challenges, such as pyometra, a dangerous uterine infection that commonly affects older unspayed females. Pyometra requires immediate medical intervention and surgical removal of the infected uterus.
Beyond reproductive health, neutering can contribute to improved behavior and quality of life for pets. Neutered animals tend to exhibit fewer aggressive and territorial tendencies, resulting in reduced incidents of fighting and marking territory. This not only safeguards the pet’s well-being but also fosters a safer and more harmonious environment for pet owners and their communities.
In conclusion, this procedure plays a pivotal role in preventing a range of reproductive-related health issues in both male and female animals. By significantly decreasing the risk of various cancers, infections, and disorders, it’s not only promotes the physical well-being of pets but also ensures a longer and healthier life. Pet owners who choose to neuter their animals are making a proactive and responsible decision that reflects their commitment to the overall health and happiness of their beloved companions.
9. Ethical Considerations and Responsible Pet Ownership: The Neutering Debate
The topic of neutering sparks an ongoing debate within the realm of responsible pet ownership, bringing to light a complex interplay of ethical considerations. It is the surgical procedure involving the removal of an animal’s reproductive organs, has both staunch advocates and vocal critics, each presenting compelling arguments from various perspectives.
Population Control and Overpopulation Crisis: One of the most significant ethical arguments in favor of neutering lies in its crucial role in curbing the rampant issue of pet overpopulation. Unplanned breeding often results in a surplus of homeless animals, leading to overcrowded shelters, euthanasia, and a strain on available resources. It helps address this crisis by preventing unintended litters, thereby reducing the number of animals in need of homes.
Balancing Individual Rights and Welfare: Critics of this procedure often emphasize the importance of respecting an animal’s autonomy and bodily integrity. Some argue that the decision to alter an animal’s reproductive organs should be made with careful consideration of their well-being and natural instincts. These individuals stress the significance of allowing animals to express their natural behaviors, including mating and reproduction.
Health Benefits and Risks: Another dimension of the ethical debate surrounds the potential health benefits and risks associated with neutering. Advocates assert that neutering can reduce the risk of certain reproductive-related health issues, such as uterine infections and certain types of cancer. On the other hand, critics point to emerging research that suggests neutering may also be linked to an increased risk of certain health problems, including orthopedic issues and certain cancers, particularly in certain breeds.
Responsible Ownership and the Greater Good: The ethical considerations surrounding neutering extend to the broader concept of responsible pet ownership. Proponents argue that responsible pet guardianship includes making informed decisions that prioritize the welfare of individual animals and the larger community. This procedure is seen as a proactive step in preventing unplanned litters, ensuring animals receive appropriate care, and reducing the burden on animal shelters and rescue organizations.
In conclusion, the neutering debate underscores the multifaceted nature of responsible pet ownership. Ethical considerations encompass a range of factors, including population control, individual welfare, health implications, and societal responsibility. As pet owners, veterinarians, and animal welfare advocates navigate this complex landscape, thoughtful discussions and evidence-based decisions play a pivotal role in shaping the future of neutering practices and their ethical implications. Ultimately, the goal remains to strike a balance between individual rights and the greater good, all while prioritizing the well-being of our beloved animal companions.
10 Important Types Of Rabbit
10. Promoting Neutering Awareness: Supporting Animal Welfare and Responsible Pet Guardianship
In today’s society, where the bond between humans and their animal companions is cherished, the concept of responsible pet guardianship has gained paramount importance. At the heart of this ethos lies the practice of this procedure , a proactive step that not only benefits individual pets but also contributes significantly to animal welfare and the broader community.
Neutering, encompassing both male and female sterilization procedures, stands as a cornerstone in the pursuit of controlling pet overpopulation. The sad reality of countless homeless animals languishing in shelters or roaming the streets underscores the urgency of addressing this issue. By opting for neutering, pet owners play a pivotal role in preventing unplanned litters, reducing the burden on shelters, and curbing the cycle of homelessness and euthanasia.
Beyond population control, it holds tangible health and behavioral advantages. In males, neutering can mitigate the risk of testicular cancer and reduce the likelihood of certain prostate issues. In females, it eliminates the potential for uterine infections and drastically lowers the risk of mammary tumors. Furthermore, neutering often leads to calmer and more well-mannered behavior, making pets more adaptable and less prone to aggressive tendencies.
Raising awareness about neutering is essential to dispel prevailing misconceptions. Concerns about the impact on a pet’s personality or the belief that every animal should experience parenthood are some of the myths that can be debunked through education. Responsible pet guardianship entails making informed choices in the best interests of the animal, including considering their health, longevity, and quality of life.
Effective promotion of neutering awareness involves collaboration between veterinarians, animal welfare organizations, and communities. Informative campaigns, workshops, and accessible resources can empower pet owners with the knowledge they need to make responsible decisions. Financial assistance or incentives can also play a role in ensuring that neutering remains an accessible option for all pet owners, regardless of their economic circumstances.
In conclusion, promoting neutering awareness transcends the realm of a simple surgical procedure. It is a collective effort to safeguard the well-being of animals, alleviate the strain on animal shelters, and cultivate a culture of responsible pet guardianship. By embracing neutering as a vital component of compassionate pet care, we pave the way for healthier, happier pets and a more compassionate society at large.
FAQ’s:
What is neutering, and how does it differ from spaying?
Neutering refers to the surgical removal of reproductive organs in animals, typically involving the removal of testicles in males and ovaries and sometimes the uterus in females. Spaying specifically refers to the removal of the ovaries and uterus in female animals.
At what age should I neuter my pet?
The ideal age for neutering can vary based on the species, breed, and individual animal. In general, most veterinarians recommend neutering cats and dogs around six months of age, but some factors, such as health and breed considerations, might influence the timing.
What are the health benefits of neutering pets?
Neutering can offer several health advantages, such as reducing the risk of certain cancers, preventing reproductive organ infections, and addressing behavioral issues. Male animals may experience a decreased risk of testicular cancer, while females benefit from a lower chance of uterine infections and mammary tumors.
Will neutering change my pet’s behavior?
Neutering can influence behavior by reducing certain hormonal-driven tendencies, such as roaming, marking territory, and aggression. While it may not entirely eliminate all behavioral issues, it often leads to a more balanced and manageable demeanor in pets.
Is neutering reversible?
Neutering is generally considered a permanent procedure, and the reproductive organs are removed. While there are some experimental techniques aimed at reversing sterilization, they are complex and not widely available. Therefore, it’s essential to approach neutering as a permanent decision for your pet’s well-being.
![20 Pretty Small Yellow Birds You Should Know [2023]](https://vetpomedix.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/20-Pretty-Small-Yellow-Birds-You-Should-Know-2023-150x150.jpg)
